National Hemophilia Foundation recommends recombinant factor as the standard of choice for treatment of hemophilia, but did you know that many factor products used to treat
hemophilia are developed from human blood, specifically human plasma? In fact, one person with hemophilia can require up to 1,200 plasma donations for a one year’s supply of factor
products. Plasma products are especially important for those undergoing immune tolerance therapy to treat inhibitors, for those with von Willebrand disease and for those in developing countries.
And plasma can come from you! Think of making a blood donation, during this time of Thanksgiving and holidays.
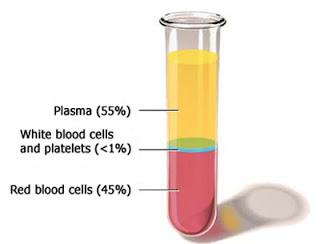
First, learn a bit more about plasma, Plasma is the straw-colored liquid that makes up
approximately 55 percent of total blood volume. A single liter of plasma yields
coagulation factors essential for blood clotting, immunoglobulins used to
combat viruses and bacterial infections, and albumin, a major plasma protein
that regulates blood volume and other essential functions.
In addition to treating hemophilia, plasma-derived therapies
are used in everyday medicines, emergency and critical care situations, as well
as preventive medicine. Albumin, for example, is used to treat burns, shock,
trauma, liver conditions and cardiopulmonary illnesses; immunoglobulins are
indicated for Rh incompatibility, pediatric HIV, hepatitis, and animal bites.
Plasma is an expensive raw material and represents between 40 to 60 percent of the cost
of plasma-derived product production. This is due primarily to its biologic
nature: plasma protein therapies are not interchangeable, have no generic
variations or substitutions, and are defined as sole-source biologic products
by global regulators.
Since plasma is biological in nature, complex regulation and
oversight measures are in place—including collection, processing, and storage
and handling requirements—to ensure plasma donor health, as well as product
purity and efficacy for patients.
The majority of the world’s plasma comes from plasma donors
in the U.S. Collectively, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and its Center
for Biologics and Research (CEBR) are responsible for regulatory oversight of
the U.S. blood supply. Blood collection centers are either registered or
licensed by the FDA, and are held to quality standards comparable to those of pharmaceutical
manufacturers. Blood establishments located outside of the U.S. that import or
offer for import blood products are also required to register with the FDA.
CEBR regulates the collection of blood and blood components
used for transfusions, as well as for the manufacture of pharmaceuticals
derived from blood and blood components. CEBR develops and enforces quality
standards, inspects blood establishments and monitors reports of errors,
accidents and adverse clinical events.
Manufacturing processes begin with fractionation,
followed by purification and virus inactivation. Fractionation is a time
consuming and complex process that extracts, or “fractions off,” specific
plasma proteins that have a proven health benefit. Fractionation requires
multiple processing steps, which involve manipulating solution pH, temperature,
ionic strength and alcohol concentration.
Once fractionated, plasma proteins are further subjected to
virus inactivation, a complex purification processes that includes prion
removal, nanofiltration, solvent/detergent
treatments and incubation, to ensure sterility and purity of the final product.
The complete manufacturing process, from plasma collection at a donor
center to the FDA’s lot release, takes seven to 12 months.
So donate now! Next year at this time, your donation could be used to save a life!
Sponsored by ASD Healthcare.
Great Book I Just Read
 The Climb to Hell
The Climb to Hell [Kindle]
Jack Olsen
Olsen sure can write a page-turner. In 1957, one of the most audacious and stunning rescues to ever take place occurred on the north face of the Eiger, one of the most notoriously difficult challenges to scale, located in the heart of the Swiss Alps. The Eiger is feared for its avalanches, fast-changing weather, and sheer facade. When two poorly-prepared Italians set off to make history by being the first Italians to scale it, they become stuck for eight days, in zero-degree weather, unable to get off the mountain. This launches an international rescue effort, that leads to surprising outcomes, including national rivalry, clashing personalities, extreme risk taking and uncertain success. Fantastic story, well told and must-reading by all mountaineers. Four/five stars.
 Read about past interns’ experience here!
Read about past interns’ experience here!