admin
November 27, 2023
This is a paid public announcement from CSL Behring and does not constitute an endorsement of products or services. When you click on the links in this blog entry, you will be directed to the CSL Behring website. LA Kelley Communications always advises you to be a savvy consumer when contacting any company; do not reveal identifying information against your will.
Hemophilia is a genetic condition
Both hemophilia A and B are caused by mutations in the gene for blood clotting factor. Hemophilia A is caused by a mutation in the gene that creates factor VIII (FVIII) and hemophilia B is caused by a mutation in the gene that creates factor IX (FIX). Both the F8 and F9 genes are located on the X chromosome at different points.
Low factor levels lead to the inability of blood to clot, resulting in numerous physical and lifestyle burdens, including unexpected breakthrough bleeds and other chronic health problems. Over half the people with hemophilia A or B have factor levels less than 1% of normal.
Gene therapies for hemophilia A and B target different genes
Gene therapy is a long-term treatment option for people with hemophilia that offers extended bleed protection, which could eliminate the need for prophylaxis. Gene therapy uses an innovative approach that redefines treatment by either introducing a functioning gene into the body, or turning off or changing the gene that is causing the condition. Current gene therapies approved for hemophilia introduce a new, fully functioning gene into the body. The mutations causing hemophilia A and B have been characterized in thousands of people, and it is clear from the large number of mutations that the molecular basis of the condition is extremely diverse.
There are differences between gene therapies for hemophilia A and B
All gene therapy for hemophilia targets the liver. However, since there are differences in how the body produces FVIII and FIX, there are also fundamental differences in how gene therapy works in the liver.
For people with hemophilia B, gene therapy targets liver cells, known as hepatocytes, where factor IX proteins are naturally made. By delivering a functional F9 gene straight to the liver, it enables a person to start creating their own factor IX proteins that are missing or not working and causing the disorder.
In hemophilia A, a functional F8 gene is delivered to the liver, allowing it to start creating the missing or nonworking factor VIII proteins that cause the disorder. However, the way gene therapy for hemophilia A works is slightly different, since FVIII is produced by different liver cells and tissues than those that produce FIX. The F8 gene is larger and structurally complex, which creates additional challenges.
How gene therapy works
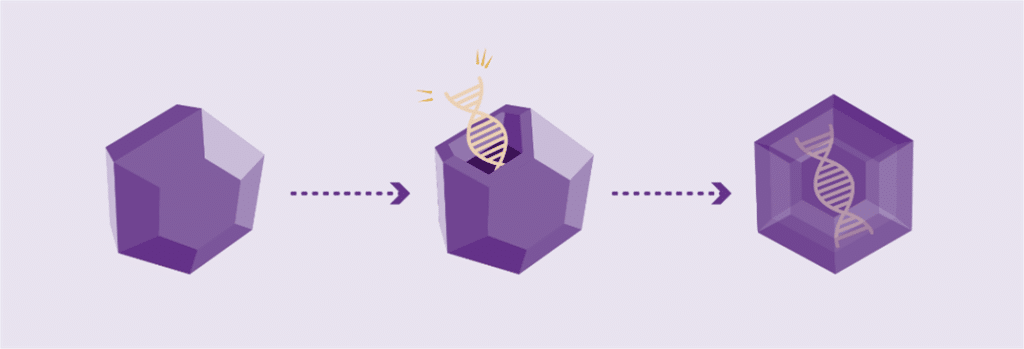
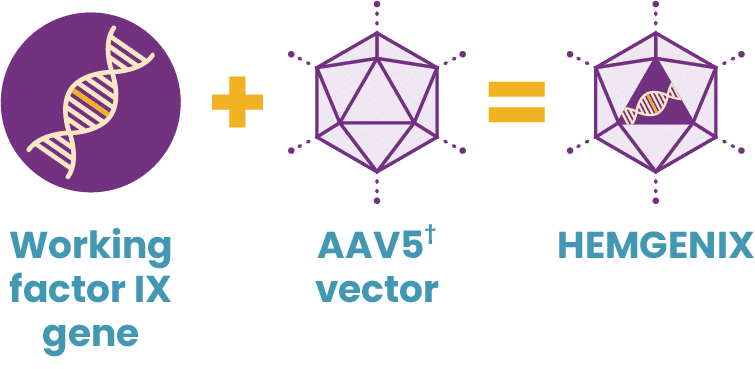
Working genes are usually delivered into the cells of the body by inserting them into an inactive viral shell, known as the vector.
Vectors being used in research are commonly made from adeno-associated viruses (AAVs). The AAV, naturally existing in the world at large, is deactivated, eliminating its ability to cause any illness while it performs its new task to deliver a therapy. In AAV-based gene therapy or gene transfer, a working gene is inserted into an AAV vector. An AAV vector protects and delivers the new gene to its destination through a one-time infusion. Current gene therapies for hemophilia A and B use different AAV vectors to deliver that new gene.
The size and simplicity of the F9 gene made it a promising target for gene therapy
Hemophilia B has long been a promising target for gene therapy because it is caused by a single gene mutation, which is both small in size and structurally simpler in comparison to hemophilia A.
In 2022, HEMGENIX®, etranacogene dezaparvovec-drlb, was approved by the FDA as the first and only gene therapy for hemophilia B. A one-time dose of HEMGENIX has been shown to offer elevated factor IX levels for years, with 37% average factor IX activity sustained at 2 years. HEMGENIX also offers greater bleed protection than prophylaxis. In a clinical trial, annualized bleed rate (ABR) for all bleeds decreased by 54% from an average of 4.1 for patients on prophylaxis during the lead-in period to 1.9 in months 7–18 after treatment. And 94% of, or 51 out of 54, people remained entirely free of continuous routine factor IX prophylaxis.
Hemophilia A has been a more challenging target for gene therapy
Due to constraints with AAV vectors, hemophilia A proved to be a challenging target for gene therapy. However, that changed recently, when the first gene therapy for hemophilia A was approved by the FDA. Administered as a single dose, gene therapy for hemophilia A has been shown to increase blood levels of factor VIII and reduce the risk of uncontrolled bleeding vs prophylaxis.
With gene therapies being approved for both hemophilia A and B, the future treatment landscape has irrevocably changed for anyone managing the condition.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What is HEMGENIX?
HEMGENIX®, etranacogene dezaparvovec-drlb, is a one-time gene therapy for the treatment of adults with hemophilia B who:
- Currently use Factor IX prophylaxis therapy, or
- Have current or historical life-threatening bleeding, or
- Have repeated, serious spontaneous bleeding episodes.
HEMGENIX is administered as a single intravenous infusion and can be administered only once.
What medical testing can I expect to be given before and after administration of HEMGENIX?
To determine your eligibility to receive HEMGENIX, you will be tested for Factor IX inhibitors. If this test result is positive, a retest will be performed 2 weeks later. If both tests are positive for Factor IX inhibitors, your doctor will not administer HEMGENIX to you. If, after administration of HEMGENIX, increased Factor IX activity is not achieved, or bleeding is not controlled, a post-dose test for Factor IX inhibitors will be performed.
HEMGENIX may lead to elevations of liver enzymes in the blood; therefore, ultrasound and other testing will be performed to check on liver health before HEMGENIX can be administered. Following administration of HEMGENIX, your doctor will monitor your liver enzyme levels weekly for at least 3 months. If you have preexisting risk factors for liver cancer, regular liver health testing will continue for 5 years post-administration. Treatment for elevated liver enzymes could include corticosteroids.
What were the most common side effects of HEMGENIX in clinical trials?
In clinical trials for HEMGENIX, the most common side effects reported in more than 5% of patients were liver enzyme elevations, headache, elevated levels of a certain blood enzyme, flu-like symptoms, infusion-related reactions, fatigue, nausea, and feeling unwell. These are not the only side effects possible. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect you may experience.
What should I watch for during infusion with HEMGENIX?
Your doctor will monitor you for infusion-related reactions during administration of HEMGENIX, as well as for at least 3 hours after the infusion is complete. Symptoms may include chest tightness, headaches, abdominal pain, lightheadedness, flu-like symptoms, shivering, flushing, rash, and elevated blood pressure. If an infusion-related reaction occurs, the doctor may slow or stop the HEMGENIX infusion, resuming at a lower infusion rate once symptoms resolve.
What should I avoid after receiving HEMGENIX?
Small amounts of HEMGENIX may be present in your blood, semen, and other excreted/secreted materials, and it is not known how long this continues. You should not donate blood, organs, tissues, or cells for transplantation after receiving HEMGENIX.
Please see full prescribing information for HEMGENIX.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch , or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
You can also report side effects to CSL Behring’s Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958.
HEMGENIX is manufactured by uniQure Inc. and distributed by CSL Behring LLC.
HEMGENIX® is a registered trademark of CSL Behring LLC.
©2023 CSL Behring LLC 1020 First Avenue, PO Box 61501, King of Prussia, PA 19406-0901 USA
www.CSLBehring.com USA-HGX-0466-NOV23